AC or DC battery: what is the difference?

The importance of efficient energy storage technologies is growing as the energy transition progresses. This is especially true for rooftop and commercial photovoltaic installations, which generate electricity during periods of high sunshine but cannot always be used immediately. That's where electricity storage systems come in. They allow self-generated electricity to be stored temporarily and used later. However, it's important to note that not all electricity storage systems are the same. There are different variants and technologies available.
There are two types of batteries: AC and DC. While AC batteries store alternating current, DC batteries use direct current. Both systems have their own advantages and disadvantages, which should be understood in order to make the best choice for your individual needs.
This article outlines the differences, operating modes, and potential applications of AC and DC batteries. The aim is to provide a basis for informed decision-making.
What is an electricity storage device and what is it used for?
An electricity storage device is primarily a technical solution for storing electrical energy. It allows self-generated electricity to be used regardless of when it is produced. This is particularly advantageous when using photovoltaic systems, as electricity production depends on the amount of sunlight available at any given time and varies accordingly. A storage device compensates for these fluctuations and maximises self-consumption by storing surplus electricity for later use.
What are the advantages of an electricity storage device?
Storing electricity in a battery has certain advantages, particularly in terms of self-consumption and savings on electricity costs.
- · Increased self-consumption & cost savings: Self-generated electricity can be used even when the sun is not shining. As a result, less electricity needs to be fed into the public grid and more electricity can be consumed on site. Since feed-in tariffs are significantly lower than the usual electricity prices per kWh, self-consumption saves a lot more money.
- · Independence from the electricity grid: reduced dependence on energy suppliers and electricity price increases, as less electricity needs to be purchased from the supplier. Every kilowatt hour produced and consumed by the company increases its independence from electricity suppliers.
- · Emergency power supply: Some systems offer the option of supplying electricity in the event of a power failure. Of course, additional technical installations are usually required for this, but as a rule, the additional costs and effort are manageable. In the event of a power failure, a household can thus continue to be supplied with energy.
- · Sustainability: More efficient use of renewable energies reduces the ecological footprint. The more solar electricity can be used, the less climate-damaging energy needs to be extracted from fossil raw materials such as coal or oil. This directly saves emissions and CO2 and reduces the impact on the climate and the environment.
Thanks to AC or DC batteries, households equipped with photovoltaic systems in particular can store surplus solar electricity during the day and use it in the evening or during periods of low sunlight. However, households are not the only ones using energy storage systems: businesses are also increasingly relying on energy storage to reduce their operating costs and optimise their energy supply.
Find the right energy storage system for your solar installation or plug-in solar panel . At Zendure, you can choose from a wide range of AC and DC models. These include the SolarFlow 800 Pro and the SolarFlow 2400 AC.
AC and DC batteries: definition and differences
The two types of batteries differ mainly in the way they store electricity. While devices with AC technology rely on storing alternating current, DC devices rely on direct current. Both forms of storage have different advantages and disadvantages.
What is an AC battery?
An AC battery (also known as an alternating current accumulator) is an energy storage device that only stores electrical current after converting the direct current from the photovoltaic system into the alternating current commonly used in households. The conversion is carried out by means of an inverter, so that the storage battery can be installed flexibly at a later date, independently of the existing solar installation.
This is not entirely true, however, as the AC battery also stores direct current. The incoming AC (alternating current) that has already been converted as described above is converted back into direct current by an inverter in the storage unit. For a PV system, this generally means that the electricity generated is available as direct current and is converted into alternating current by an inverter. The alternating current then flows into the storage battery, where it is converted back into direct current and stored.
Features of an AC battery:
- ● Can be installed independently of the PV system
- ● Ideal for upgrading an existing solar system
- ● An inverter is required to convert direct current into alternating current
- ● Higher conversion losses due to multiple conversions
- ● Can also absorb energy from the grid
- ● Suitable for peak/off-peak hours
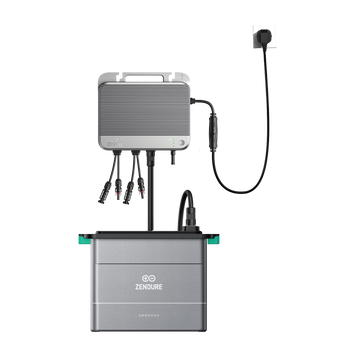
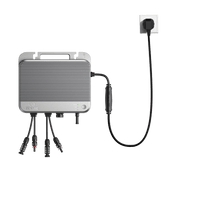
Tip: The new Zendure SolarFlow 2400 AC storage unit is not just AC-compatible electricity storage. The device can also store electricity from the grid, making it ideal in combination with off-peak hours offered by many energy suppliers.
The Zendure SolarFlow 2400 AC is an AC-coupled energy storage system that intelligently integrates into your home network. Through AC coupling, it can efficiently store electricity from the grid (including your PV inverter) and release it as AC power when needed. Although AC coupling requires two conversions, Zendure achieves AC round-trip efficiency of up to 93% thanks to advanced SiC semiconductor technology. Its main strengths lie in its excellent compatibility and flexibility; it can be easily added without modifying the existing photovoltaic system, making it particularly suitable for households that have already installed solar panels but wish to increase their energy self-consumption rate. In addition, the SolarFlow 2400 AC also supports grid charging, enables various use scenarios such as low-level energy storage and backup power supply, and can also operate independently without a photovoltaic system.
What is a DC battery?
On the other hand, a DC (direct current) battery directly stores the direct current produced before it is converted into alternating current, which is more common in households. This generally results in less energy loss, as only one conversion is required.
Features of a DC battery:
- · Can be connected directly to a photovoltaic system (use of direct current).
- · Lower conversion losses, as storage is direct in the form of direct current.
- · Generally more cost-effective in a new installation, as no additional inverter is required.
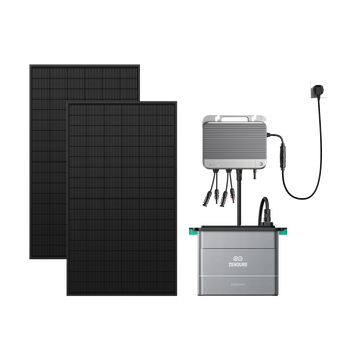
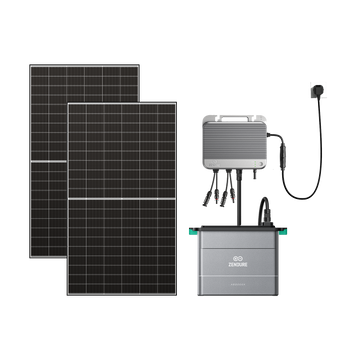
The Zendure SolarFlow 800 Pro is an efficient 800W micro-inverter with integrated DC memory that connects directly to solar panels. It prioritises charging batteries with solar energy and only requires DC-AC conversion during discharge. Thanks to 48V technology and GaN components, it achieves a peak efficiency of up to 96%. Even smarter, it supports bidirectional charging and discharging, allowing you to store electricity from the grid when electricity prices are low and release it during peak hours to save even more on electricity costs. The SolarFlow 800 Pro is the ideal choice for a plug-in solar panel that will help you optimise your energy use and reduce your costs!
Direct comparison of AC and DC batteries
|
Criteria |
AC battery |
DC battery |
|
Installation |
Easy to retrofit |
Ideal for new installations |
|
Conversion losses |
Higher losses due to double conversion (DC → AC → DC → AC) |
Lower cost, as only one conversion (DC → AC) is required |
|
Costs |
Purchase cost often higher |
More cost-effective for new buildings |
|
Compatibility |
Can be operated independently of the solar installation |
Must be adapted to the PV installation |
Which is bettery – AC or DC?
The choice between an AC or DC accumulator depends largely on the type of battery used and the system best suited to the existing or planned photovoltaic installation.
Advantages and disadvantages of AC-coupled batteries
AC batteries are flexible to use and can be installed independently of the solar installation. They are ideal for equipping an existing photovoltaic installation, as they can be easily integrated into the existing electrical network.
Advantages: One of the major advantages of AC solutions is that they can be retrofitted and operate independently of an existing photovoltaic system. In addition, this variant is compatible with various inverters and is suitable for use with dynamic electricity tariffs.
Disadvantages: Among the disadvantages are slightly higher conversion losses, as the current has to be converted twice – from direct current to alternating current – and back again. In addition, the additional inverter results in slightly higher costs.
Advantages and disadvantages of DC-coupled batteries
DC batteries work directly with the direct current produced by solar panels. Electricity can thus be stored more efficiently before being converted into alternating current. This solution is particularly suitable for new buildings or when a new photovoltaic installation is planned.
Advantages: This variant has the advantage of reducing energy losses by performing only a single conversion, making it particularly efficient. For new installations, it is also cost-effective and allows direct coupling with the solar installation.
Disadvantages: Retrofitting is more challenging, however, as it requires a direct connection to the photovoltaic system. While it's possible to save on the additional inverter (compared to the AC variant), installation costs are often higher. Furthermore, this solution is less flexible in its application.
AC or DC: what type of storage do I need?
The choice between an AC or DC battery depends on various factors that must be assessed individually. Here are the main criteria to consider when choosing:
Existing or new photovoltaic installation?
In the case of an existing PV installation, it is generally recommended to use an AC battery, as it can be easily upgraded and operates independently of the existing inverter. However, if a completely new installation is planned, a DC battery is often the best choice. It operates more efficiently and can be directly connected to the photovoltaic installation.
Flexibility and usage behaviour
Both systems help maximise self-consumption, but DC batteries are particularly efficient due to their reduced energy losses. If you want to have a backup power supply, many AC batteries already have a built-in backup power function. In terms of flexibility, AC systems also have a major advantage, as they are easier to expand or adapt.
Technical requirements
AC batteries require their own inverter, which is not usually a problem for existing installations. On the other hand, when planning a DC battery, it is necessary to check whether the existing inverter is compatible. In terms of space and installation, DC batteries can be slightly more compact, but they generally require more careful planning and coordination of components.
Budget
AC batteries are often slightly more expensive to purchase, but they are easier to install.
If you are looking for a flexible and affordable AC battery, the SolarFlow 2400 AC from Zendure is a bidirectional AC battery with a backup function and plug-and-play design for simple and flexible installation.
Installing an AC battery – What should you bear in mind?
Adding an AC battery is an attractive option for effectively expanding existing photovoltaic systems and significantly increasing self-consumption. However, there are a few things to consider to ensure that the retrofit goes smoothly:
1. Check compatibility
Not all batteries are compatible with all photovoltaic systems. Before choosing an AC battery, you should check whether your existing photovoltaic system and inverter meet the technical requirements of the desired battery.
2. Assess the electrical infrastructure
It is advisable to have the domestic connection and electrical distribution assessed by a professional electrician. Some batteries require additional protection or space in the fuse box.
3. Consider the space required
AC batteries require a certain amount of space in the house or basement, depending on the model and capacity. Installation should be as close as possible to the grid connection point in order to minimise line losses.
4. Calculate installation costs
In addition to the battery itself, there are also costs for installation, electricity and, if necessary, conversion. An individual quote from a certified installation company will give you the total price.
5. Consider extension options
Some AC batteries can be extended in a modular fashion. If you are considering expanding your photovoltaic installation or storage system in the future, it is important to choose a compatible system from the outset.
Which is more advantageous – an AC or DC battery?
A crucial factor in choosing between an AC and DC battery is cost. This consists of both the acquisition and installation costs on the one hand, and the operating costs on the other. Any subsidies also play an important role in calculating the costs of an electricity storage system.
Acquisition costs
AC batteries usually have their own inverter and are slightly more expensive to purchase, but they are particularly well suited to existing PV installations – ideal for upgrades. DC batteries, on the other hand, can be efficiently integrated into the overall system of new construction projects, often reducing overall costs and increasing system efficiency.
Installation costs
AC systems are attractive due to their modular design and are easy and simple to install, especially in existing installations. DC systems, on the other hand, require more precise planning and coordination with the PV installation, which can increase installation costs – but they offer a more efficient overall solution for new installations.
Operating costs and efficiency
AC batteries lose a bit more energy because they convert DC to AC and back again, which can affect efficiency and cost-effectiveness over time. DC batteries are more efficient because they store electricity directly, minimising conversion losses and saving energy over the years.
Long-term profitability
While AC batteries may be slightly more expensive to purchase, they offer a good retrofit option thanks to their flexibility. DC batteries, on the other hand, score points for lower operating costs and greater efficiency, which is particularly attractive for new builds or major retrofits.
Conclusion: AC or DC battery – Which is the best choice?
Choosing between an AC or DC battery depends on the existing or planned photovoltaic installation. AC batteries are well suited for retrofitting existing installations, but they are less efficient due to higher conversion losses. DC batteries are more efficient for new installations because they store direct current directly, but require more precise planning.












































































































Leave a comment